| Broadband | ||||
|
The capacity of a communications channel is called its bandwidth.
The higher the bandwidth, the more data can be transferred in a given
time. |
||||
| Bandwidth is usually measured in bps
(bits per second). |
1 kbps = 1024 bits per second. | |||
| Broadband is
a technology that allows many signals to be carried along a communications
link at the same time. This greatly increases the bandwidth
and allows high-speed transmission of data along a network.
The bandwidth of broadband connections is usually measured in Mbps.
|
1 Mbps = 1048576 bits per second | |||
| Types of broadband :
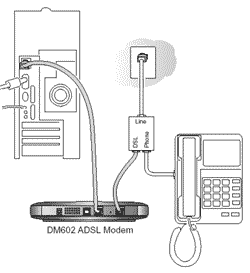
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) uses a nationwide network of digital links. There is no need for a modem. ISDN links are being replaced by faster methods such as ADSL. ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) uses the existing telephone lines to send digital signals. Downloading data is faster than uploading. ADSL links can be left permanently connected to the Internet, improving speed of access to information and allowing emails to be delivered immediately. ADSL links require a special modem.
|
A modem converts a computer's digital signals into analogue signals as used by the telephone system...and back. | |||
|
|
An ADSL modem is needed to connect to the telephone socket. | |||
| Cable. many homes have a cable connection for television and these can also be used to connect to the Internet. | ||||