| [1](a) | School students are to be surveyed to find
out if they will be applying to university.
Name a suitable data type for storing each of the following, giving a reason for your choice in each case:
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | the number of A level subjects the student is taking; | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | whether the student is intending to apply to university or not; | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iii) | the mean mark gained in school examinations, for instance 62.4; | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iv) | the student's home telephone number, for instance 01970 123456. | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (b) | State one data structure which could store all four items of data given in part (a) for one student as a single item. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [2](a)(i) | A computer program includes a line in which a command word is misspelled. What type of error is this? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | Another program is correctly written but fails to run correctly. What type of error is this? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iii) | Another program appears to run correctly, but its output is wrong because it contains an incorrect calculation. What type of error is this? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (b) | What is the function of a translation program when applied to a source program? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [3] | A firm sends letters to members of the public.
It does this by combining name and address data from one part of an
integrated package, into a standard letter produced in another part of
the same package.
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | What name is given to the operation when data are combined in this way? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | What two parts of the integrated package would be useful for this operation? | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [4](a) | A computer program runs through a list of
numbers, comparing each number against a fixed number until either a
match is found or the end of the list is reached.
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | Is this operation a sort or a search? State what type of sort or search it is. | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | If the number is not matched, what should happen when the end of the list is reached? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (b) | Under certain circumstances, a binary search can be used. | |||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | When can it be used, what is the benefit of using a binary search over other types of search? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | Under what circumstances can a binary search be used? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [5](a) | A systems analyst can use a number of
techniques to find out how an existing system works. These include:
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | Describe one advantage of using questionnaires over interviewing staff. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | State two other methods which might be used to find out about the current system. | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iii) | The systems analyst produces a requirements specification. Describe two elements which this should contain. | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (b) | Describe two activities which should take place during the testing of a new computer system. | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (c) | For a new computer system to be successful, it needs to be cost effective. State one other basic requirement. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [6] | Languages such as HTML are used in the development of web pages. describe two features which make such languages suitable for this purpose. | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [7] | One type of software is applications software. | |||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | Describe what is meant by the term applications software. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | Give an example of applications software. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iii) | State another type of software. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iv) | Give an example of the type of software you stated in part (iii) | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
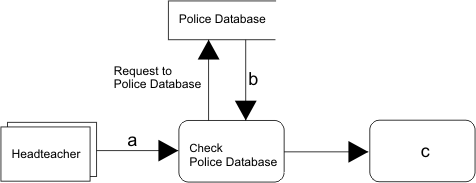
| [8] | Before a teacher can be employed at a school,
the headteacher has to check whether the teacher has a criminal record.
In every case, after this check, the teacher receives a letter stating
whether he or she has been successful or not.
This situation is shown in the diagram below. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | This diagram is called a data flow diagram. Give two reasons why data flow diagrams are useful during systems analysis. | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | What type of object does the open box in the diagram represent? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iii) | What type of object does the shadow box in the diagram represent? | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (iv) | Give a suitable name for the object shown as a in the diagram. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (v) | Give a suitable name for the object shown as b in the diagram. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (vi) | Give a suitable name for the object shown as c in the diagram. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [9](a) | Describe what is meant by the term global variable in a computer program. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (b) | Describe what is meant by the term local variable in a computer program. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| [10] | A train company uses an algorithm to determine
whether a journey is peak or off-peak.
On weekdays, early morning journeys are charged at full price (peak).
After a certain time in the morning, journeys are charged at a reduced
rate (off-peak). At weekends all journeys
are off-peak. Currently, the month of
travel makes no difference to the price charged, although it is input to
the algorithm.
The algorithm used is shown below: |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (i) | State what the output will be if the three inputs are: | [3] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (ii) | A change is made in line 5 so that it now reads: | |||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| I | Explain the difference this represents to the company's charging policy. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| II | Give an example of data which illustrate this difference. | [1] | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 11. | In the following
question, additional credit (up to 3 marks) will be given if your answer
demonstrates skill in written communication.
|
[8+3] | ||||||||||||||||||
| The computer section of a large company is
intending to replace an existing computer system. The programmers plan
to use a top-down design method, and use standard
modules. When the
system is completed, the company intends to use a direct
changeover.
The company is very concerned to design a human-computer interface (HCI) which is easy-to-use for non-experts and to ensure that the system will be easily maintainable. Describe in detail why the company might wish to use a top-down design method and standard modules, and also a direct changeover. Also describe in detail how they might achieve a system which has an easy-to-use HCI and which is easily maintainable.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
A top-down design method
successively breaks a large task into a number of smaller tasks, making
the development of a new system much easier for the programmers.
Standard modules consist of previously developed subroutines that can be
used in any software the programmers write. As they have been previously
tested, they are guaranteed to work and will save time for the
programmers.
A direct changeover of systems involves stopping the old system and starting the new one immediately. The changeover would be completed quickly, but there may be problems if parts of the new system fail to operate correctly. An easy-to-use HCI would involve the use of a GUI - a graphical user interface where icons (small pictures) are used to convey the purpose of buttons and applications. For example a picture of a printer may appear on a 'Print' button. Consistent use of these icons means that users will find the software easy to learn to use. Software will be easily maintainable if the programmers provide adequate documentation, giving details about the programs and the variables used. The names of variables should be meaningful and the programming code should be fully annotated.
|
||||||||||||||||||||