| [1](i) |
State the computer term for an area of memory where data
is temporarily stored while being transferred between a keyboard and a
computer.
|
[1] |
| |
|
|
| (ii) |
Give a different example of where such an area of memory
would be used in a computer system, stating clearly the relative speeds
of the devices concerned. |
[2] |
| |
- when data is saved to a hard disc, it is
transferred to a buffer first...
- ...because the speed of the hard drive is much
slower than the speed of the processor.
|
|
| |
| [2](a) |
Wide area networks can use circuit
switching or packet switching to
transmit data from a source work station to a destination work station. |
|
| (i) |
Explain in detail how data is
transmitted from source to destination using circuit
switching. |
[2] |
|
- a connection is made between the two work
stations by switching all the switches on..
- ..and then the data is sent directly along
the circuit
|
|
| (ii) |
Explain in detail how data is
transmitted from source to destination using packet
switching. |
[3] |
|
- the data at the source is split into a
number of packets of data
- each packet has the address of its
destination and is transmitted from workstation to workstation until
it reaches its destination. Not all packets need follow the same
route.
- the destination workstation reassembles
the data from all the packets it receives
|
|
| (iii) |
State one advantage of using
packet switching rather than
circuit switching. |
[1] |
|
- more reliable - if one workstation goes
down, the data can still be sent via another route.
|
|
| (b) |
A ring network uses a token to communicate with other
stations on the network. The token is continuously passed from station
to station. |
|
| (i) |
Give one disadvantage of a ring network topology compared
to a bus network. |
[1] |
|
- one broken section of cable causes the
whole network to break down.
|
|
| (ii) |
When data is being transmitted, the token will contain
actual data and check data. State another item that must be included in
the token. |
[1] |
|
|
|
| (iii) |
Explain in detail how data is sent from the source to the
destination using token passing on a ring network. |
[3] |
|
- source attaches the data to a token. Token
contains addresses of source and destination
- the token is continuously passed round the
network, each station checks the token and passes it on, until it
reaches its destination
- destination retrieves the data from the
token
|
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
A holiday company allows customers to search for holidays
using the company's website. After the customer has selected a holiday
they move to a new page where they can book the holiday. The master
file is then updated to indicate
that a booking has been made. A copy of every booking transaction is
stored in a separate file called a
transaction log. |
|
| (i) |
Explain how the system would stop two customers booking
the same holiday. |
[1] |
|
- As soon as a holiday is booked, one of the
fields of a record on the master file is updated to show the holiday
as being unavailable to anyone else.
|
|
| (ii) |
If the master file becomes
corrupted, the holiday company would not know which customer had booked
which holiday. Explain in detail how the transaction
log could be used to restore the corrupted master file. |
[2] |
|
- a backup copy of the master file is
loaded.
- all the transactions in the transaction
log are performed again, updating the master file.
|
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
The operating system of a multi-user computer has to
manage the computer's resources. |
|
| (i) |
Explain in detail how the
operating system uses time slicing to
allocate processor time to user tasks. |
[2] |
|
- each user's program gets a time slice - a
small (maximum) amount of processing time in turn.
- the operating system will decide the order
of processing using a system of priorities allocated to each user's
program
|
|
| (ii) |
Partitioning is used when
allocating main memory. Explain in detail the
term partitioning. |
[2] |
|
- memory is divided into partitions that are
allocated to a program when it is run.
- no program may use memory in another
program's partition.
|
|
| (iii) |
Explain the meaning of the computer term interrupt
and give two examples of situations where
interrupts may occur. |
[3] |
|
- an interrupt is a signal from a device to
the operating system.
- an interrupt occurs at the end of a time
slice of processing time to let the operating system know that it
needs to change to processing another program
- an interrupt may be received from a device
such as a printer when it runs out of paper.
|
|
|
|
|
| [5](a) |
A particular indexed sequential
file uses a three level index. Explain in
detail, with the aid of a diagram how a
record is located using the three indexes. |
[3] |
|
- First index contains ranges of keys and
location of second index.
- Second index contains smaller ranges of
keys and locations of final index
- Final third index contains keys and
physical addresses of records.
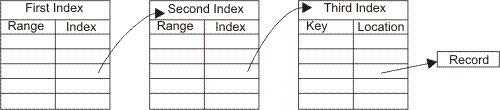
|
|
| (b) |
Give one advantage of using
an indexed sequential file rather than a direct
access file |
[1] |
|
- the file is sorted - so the records can be
processed in order.
|
|
| (c) |
Explain in detail how a
record is located using a hashing algorithm when the record is stored in
the overflow area, |
[4] |
|
- a calculation is performed on the key
field of the record to be located...
- ...resulting in the hash address of the
block where the record should be stored.
- A serial search of that block would result
in the record not being found - only the address of an overflow
area.
- A serial search of the overflow area would
result in the record being located.
|
|
| (d) |
How will accessing a record in the overflow area affect
the access time? |
[1] |
|
- it would slow the search process down
|
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
Each year students enrol on many college courses. The data
is stored in a database which has not been normalised; some of the data
is inconsistent. An example of the data is shown below. |
|
|
Student
Number |
Name |
Address |
Tel Num |
DOB |
Course Title |
Course
Cost |
Start
Date |
| 101 |
Ian Smith |
22 Apple Drive |
0111 555444 |
29/07/88 |
AS Level
Physics |
£200 |
08/09/07 |
| 101 |
Ian Smith |
22 Apple Drive |
0111 555444 |
29/07/88 |
AS Level
Chemistry |
£200 |
08/09/07 |
| 123 |
Jane Jones |
31 Farm Road |
0123 656565 |
17/03/87 |
GCSE
Mathematics |
£95 |
15/09/07 |
| 101 |
Ian Smyth |
22 Apple Drive |
0111 555444 |
29/07/88 |
AS Level
Photography |
£350 |
08/09/07 |
| 123 |
Jane Jones |
31 Farm Road |
0123 656565 |
17/03/87 |
GCSE English |
£95 |
15/09/07 |
| 123 |
Jane Jones |
31 Farm Road |
0123 656565 |
17/03/87 |
GCSE Spanish |
£95 |
15/09/07 |
| 136 |
Harry Stien |
44 Tree Street |
0499 333242 |
22/05/71 |
GCSE Spanish |
£95 |
15/09/07 |
| 123 |
Jane Jones |
31 Farm Road |
0123 656565 |
17/03/87 |
GCSE History |
£95 |
15/09/07 |
| ........ |
........ |
........ |
........ |
........ |
........ |
...... |
|
|
| (a) |
Using an example of inconsistent data from the above
table, explain what is meant by the term data
inconsistency. |
[2] |
|
- If data is stored more than once, the two
or more versions of the data may be different
- Ian Smith / Ian Smyth (one of these is
spelled incorrectly)
|
|
| (b) |
How could the possibility of this database containing
inconsistent data be removed? |
[1] |
|
|
|
| (c) |
A definition of third normal form is 'data
items are dependant on the primary key only and dependant on the whole
of the primary key'. |
|
|
Using an example from the above data, which is not
normalised, explain why this data is not in third normal form. |
[1] |
|
- The primary key is the field 'Student
Number' but there are fields stored such as 'Course Title' that do
not depend on the student number.
|
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
Car engines are controlled by a computer system called the
engine control unit
(ECU). The ECU has several inputs. |
|
| (a)(i) |
The ECU uses feed-back to
control the engine. Explain in detail what
is meant by the term feed-back |
[2] |
|
- sensors in the engine input readings to
the ECU, that may then make adjustments.
- outputs from the ECU may then affect
subsequent readings from the sensors.
|
|
| (ii) |
Describe one benefit of using
a computer system to control the engine. |
[1] |
|
- continuous and automatic monitoring of the
engine performance (no human intervention required)
|
|
| (b)(i) |
Explain the difference between analogue and digital
signals. |
[1] |
|
- digital signals have distinct discrete
values - analogue signals may have any of a range of continuous
values.
|
|
| (ii) |
One input to the ECU is the engine temperature. Explain
why analogue to digital conversion will be required to monitor the
engine temperature. |
[1] |
|
- the temperature readings will be analogue,
so they will need to be converted to digital readings for the
computer to process them. (computers process digital data)
|
|
|
|
|
| [8](a) |
Data can be transmitted along a data line in two different
ways, either one bit after the other or by simultaneously transmitting
more than one bit at the same time. State the name of each
of these data transmission methods. |
[1] |
|
- one bit after another - serial
transmission
- more than one bit at a time - parallel
transmission
|
|
| (b) |
Data can be transmitted along a data line in both
directions at the same time. State the name of this data transmission
method. |
[1] |
|
|
|
| (c) |
Explain the need for multiplexing
in a computer system. |
[1] |
|
- many signals can use the same transmission
medium
|
|
|
|
|
| 9. (i) |
A recording company has recording artists who produce
albums. Each album contains many singles and each recording artist
produces many albums. |
|
|
The company need to know which artist has released which
album and what singles are on each album. |
|
|
Design a three-table database
for recording artists, albums and singles in third normal form to handle
the information required for this application |
|
|
You should clearly indicate suitable
table names and any primary of foreign keys that you use. |
[8] |
|
- ARTISTS(ArtistID, ArtistName,
ArtistAddress, ArtistTelNum)
- ALBUMS(AlbumID, AlbumName,
ArtistID,
DateReleased)
- SINGLES(SingleID,
AlbumID, SingleName,
Time)
Underlined fields are key fields
Overlined fields are foreign fields.
|
|
| (ii) |
The recording artists also release downloads which are not
released as singles or contained on any album. Add an extra table to
your database to accommodate this extra information. |
[2] |
|
- DOWNLOADS(DownloadID,
ArtistID,
DownloadName, DownloadTime)
|
|
|
|
|
| [10] (a) (i) |
Explain what is meant by the term data
encryption |
[1] |
|
- coding of data to make it meaningless.
|
|
| (ii) |
Explain in detail how
encrypted data can be read by the appropriate person. |
[2] |
|
- the encrypted data needs to be
decrypted...
- ...using a decryption key.
|
|
| (b) |
Many large organisations carry out disaster planning for
their computer systems. Describe two
elements of disaster planning which can allow an organisation to quickly
recover following a disaster to their computer system. |
[2] |
|
- disaster prevention - precautions to be
taken before a disaster occurs such as backing up of data
- methods of recovery - after the disaster
has occurred. Eg. how to retrieve lost data
|
|
|
|
|
| 11. |
In the following question,
additional credit, (up to 3 marks) will be given if your answer
demonstrates skill in written communication. |
|
|
Engineers have designed a new aeroplane called UltraJet
that will be the biggest aeroplane ever produced. The pilots will
require training before they can fly the UltraJet prototype. |
|
|
The engineers have also used complex software and powerful
computers to create a flight-training simulator to train UltraJet
pilots. |
|
| |
Explain why powerful computers are essential for
flight-training simulators and describe the difficulties in producing a
realistic simulator. Also describe the benefits of using flight-training
simulators to train UltraJet pilots. |
[7+3] |
|
- Powerful computers are needed to process
large quantities of data being input.
- The data needs to be processed fast
because the simulator is a real-time system and must react
immediately to any inputs.
- Real life situations are extremely complex
and only an approximation to real life can ever be achieved.
- Extreme conditions such as flying the
UltraJet through a hurricane can only be simulated approximately as
realistic behaviour cannot be measured.
- There is a lot less danger for pilots to
train on a simulator, and crashing planes in reality would be an
expensive business!
- Many situations can be simulated including
difficult weather conditions such as fog, cross winds etc, so the
pilots can get practice at flying the new plane in all conditions.
- Experimentation can be carried out without
endangering aircraft or human life.
|
|
| |
