| 1(a) | Analysts and programmers sometimes need to
choose between programming languages.
For instance, a programmer might have to choose between an imperative and a declarative language. |
||||||||||
| (i) | Explain what is meant by an imperative language, and state an example of an application which could sensibly use an imperative language. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | Explain what is meant by a declarative language, and state an example of an application which could sensibly use a declarative language. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (b) | A programmer is required to write a program to
simulate the arrival of trains at a busy station. He/she has the choice of
a specialist simulation language or a general purpose language.
Describe one advantage of each type of language. |
[2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (c) | A certain programmer chooses to use an object-oriented approach, using a visual programming language. Explain the two terms object-oriented and visual programming languages and describe two advantages which their use might have over a more traditional approach. | [4] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| 2(a) | In Computer A, positive or negative integers are represented by the use of two's complementation, using 8 bits. | ||||||||||
| (i) | Show how the number +3010 is represented. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | Show how the number -3010 is represented. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (b) | In Computer B, positive or negative integers are represented by the use of 1 sign bit and 7 magnitude bits. The sign bit is the most significant bit, and is set to 1 to represent negative and set to 0 for zero or positive. Show how the number -3010 is represented in this case. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (c)(i) | Convert the number 2910 into hexadecimal. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | Binary numbers used by computers are often converted into hexadecimal numbers for the benefit of the human programmers. Describe the advantage of hexadecimal over binary for the programmer. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (iii) | These binary numbers could instead be converted into denary (base 10). Describe the advantage of hexadecimal over denary. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
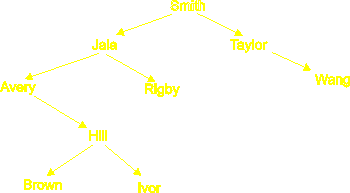
| 3(a) | The names Smith, Jala,
Taylor, Avery, Hill,
Brown, Ivor, Wang
and Rigby are to be entered in the above
order into a binary tree structure. In each case the left pointer
indicates the condition:
earlier in the alphabet. The tree structure is started below. Copy and complete the diagram. You can use just the initial letter of each name if you wish: S, J, T, A, H, B, I, W and R. |
||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| (b)(i) | Give one advantage of a binary tree structure over a linear linked list. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | Give one advantage of a linear linked list over a binary tree structure | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| 4(a) | One (not very satisfactory) way of defining a
positive decimal number is: zero or more digits, followed by a decimal point, followed by zero or more digits. For instance, the following are covered by this definition: 12.3 0.3 .3 . 2.05 12. Give an appropriate Backus Naur Form (BNF) definition for a positive decimal number as defined above, defining any terms you introduce. |
[2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (b) | The definition in part (a) is not very
satisfactory in that it allows two unusual forms:
Amend your definition so that these two forms are not allowed. |
[2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| 5(a) | Explain why a compiled program will normally execute faster than an interpreted program. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (b) | Most programming environments include some sort of debugging software. | ||||||||||
| (i) | One example of debugging software is a program trace. Explain the term program trace. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | Give an example of an error which debugging software will not be able to find. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (c) | Compilation of a high level language includes
the following processes. Describe each of these processes. |
||||||||||
| (i) | lexical analysis | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | syntax analysis | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| 6(a) | Draw up a truth table to demonstrate the EXCLUSIVE OR (XOR) operation. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (b)(i) | Carry out a bit-wise XOR operation on the
following two 8-bit binary numbers:
X = 10001011 K = 11100010 |
[2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | State what the results would be if you carried out a bit-wise XOR on your answer to part b(i) and the number K. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| 7(a) | Define the term algorithm. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (b) | Algorithms are often described using pseudocode. State two other methods of specifying algorithms. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (c) | Programmers sometimes use recursive algorithms. | ||||||||||
| (i) Describe the key features of a recursive algorithm. | [2] | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) Describe two advantages of a recursive algorithm when available. | [2] | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (d) | The following algorithm is intended to work out
the minimum number of coins required to pay any amount of cash up to
£4.99, and output a list of the required coins.
(Note : coins of the following types are available: £1 50p 20p 10p 5p 2p 1p. You should assume that there is no £2 coin available). For instance, for the amount £1.71, the algorithm will correctly output the following: £1 coin 50p coin 20p coin 1p coin |
||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| This algorithm will not work correctly for every amount up to £4.99 | |||||||||||
| (i) | Write down the output of this algorithm resulting from an input of | ||||||||||
| (I) £1.33 | [1] | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (II) £2.44 | [1] | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (ii) | To correct the algorithm, it is necessary to make one change concerning the number of £1 coins output, and also a similar change relating to two other coins. Write down the other two coins. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (iii) | Copy and amend part of the algorithm so that the correct number of £1 coins is output. (You do not need to consider the other coins you mentioned in part (ii)). | [4] | |||||||||
|
if amount_in_pence >= 100 then
output "£1 coin"; set amount_in_pence = amount_in_pence - 100; endif; should be re-written to... while amount_in_pence >=100 |
|||||||||||
| 8(a) | Most graphical user interfaces (GUIs) systems use a mouse. State why a mouse is particularly suitable for a GUI system. | [1] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (b) | Once the system has been developed, describe how its GUI system might be evaluated. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| (c) | Several of the software developers are members of a professional computing organisation, and have agreed to be bound by its Code of Conduct. Outline two relevant statements which such a Code of Conduct might contain. | [2] | |||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| In the following part-question, additional credit will be gained if your answer demonstrates skill in written communication. | |||||||||||
| (d) | A software development team has been asked to
develop a suite of technical programs for use by scientists in a
laboratory. It is intended that the package will control scientific
equipment and will record results directly. The package is required to
have an interface which uses a mixture of GUI and text-based elements.
Describe the benefits which a GUI would offer in this case and also the
possible benefits of being able to change from a GUI to a text-based
interface on occasions.
One method of input which was considered in this case but then rejected was a voice input system involving word recognition. Discuss the difficulties faced by those developing voice input systems. |
[11] | |||||||||
|
The GUI interface has clearly identifiable icons
representing different options. This makes it easy to learn for all of
the scientists in the lab, whatever level of IT skills they may have.
There will be no need for anybody to learn complex commands to
operate the software. The icons used in the GUI are similar to those
used in other standard software packages, so the users may already be
familiar with them.
The alternative text-based interface will offer a wider range of options, as each command may have a number of optional 'switches'. As it will take up less memory the software should run much faster then the GUI. The text-based program may also be set up as a batch file and run automatically under a scheduling program. Voice input may cause problems as people speak with different accents, at different speeds and possibly in different languages. There may also be problems identifying words that sound the same ('Which' and 'Witch'). People's voices may also be affected by illness - sore throat etc.. |
|||||||||||