| Input Devices |
| Keyboard |
 |
Allows characters to be input.
Used on all computers. Particularly useful in word processing and
command line OS (eg DOS) |
| Mouse |
 |
Used on PCs. Directs a screen
pointer. Used in a GUI (WIMP) environment. |
| Joystick |
 |
Used on PCs mainly for
games-playing. |
| Touch screen |
 |
User touches the
screen to select menu items etc..Often used in public places eg
libraries, museums where mouses or keyboards may be stolen. |
| Light pen |
 |
User 'writes' on
the screen with the pen. Used for some graphics
(CAD) or art packages. |
| Graphics
tablet |
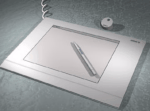 |
Used for graphics
packages to give a more natural 'feel'. User draws on tablet and results
appear on the screen. Eg - could be used for tracing maps. |
| Bar code
reader |


|
Numerical data is
coded as a sequence of lines. The reader can be passed over these lines
and using a small laser the data can be read and input to the computer.
Either built-in scanner or hand-held
'wand'.
Used in shops, supermarkets (POS systems)
libraries, and for reading ID cards. |
| OCR reader |
 |
Optical Character
Recognition.
Scans and inputs characters from a printed sheet.
Inputs text into WP or DTP.(saves a lot
of typing!). Also used for reading turnaround documents eg gas meter
reading forms. |
| Scanner |
 |
Scans and inputs
images from a printed sheet.
Hand-held or flat-bed.
|
| Digital
camera |
 |
Photos
can be downloaded into a computer and stored. |
| Mark-sense
reader (OMR) |
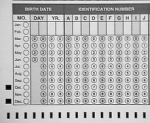 |
Optical Mark
Recognition.
Scans and inputs
data represented by marks on a sheet. Eg school registers,
multiple-choice exam papers, census forms, lottery tickets.
|
| MICR reader |
 |
Magnetic
Ink Character Recognition.
Reads data electronically off bank
cheques printed in magnetic ink using a special font. Very fast, and
reliable. Prevents fraud and can read spoilt and crumpled cheques.
|
| Speech input |
 |
Using microphones.
Commands may be 'spoken' to control the computer.
Vocabulary dictation systems use
special software to convert speech into text data. Eg dictating a letter
into a WP.
Problems -different languages/
accents/ changes in voice due to illness |
| Handwriting
recognition |
 |
The user writes with a special pen
onto a screen which detects the input. The computer often converts handwriting into typed
text. |
| Sound input |
 |
Using microphone /
tape / CD.
Eg used for recording sounds for special effects in theatres,
film studios etc.
|
| MIDI input |
 |
Musical
Instrument Digital Interface. Recording the sound patterns of
musical notes using different instruments. |
| Virtual
Reality input |
 |
Hardware devices
eg digital glove are worn by the user, whose movements are sensed and
used as input. A VR helmet may be used to project images for the user to
'interact' with. |
| Sensor input |
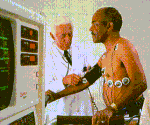 |
Digital readings
of eg light, sound, heat, movement, heart beat are measured and sent as analogue
signals to be used as input for a control system. Eg. Intensive care
patient monitoring, security system. |
| Magnetic
strip |
 |
A card with data
recorded onto a magnetic strip is 'swiped' through a card reader, and
data is read off it. |
| Smart
Card |
 |
Cards with chips
embedded into them are swiped through a special card reader. |
| Output Devices |
| Monitor |
 |
Screen displays are composed of a
large number of pixels which display 'dots' in different colours.
High-powered graphics can be used if a graphics card is fitted
into a PC.
|
| Printer |

(inkjet printer)
|
Used to create 'hard copy'.
Laser printer (top) - good
quality print; quiet.
Inkjet printer (bottom) -
cheaper; slow; can use colour.
|
| Graph Plotter |


|
Used to produce high quality graphics
for CAD applications. eg building plans; microchip designs etc
Flatbed plotter (top) or drum plotter (bottom)
|
COM
Computer Output on Microfilm/Microfiche |
 |
Output documents greatly reduced in
size onto film.
Microfilm on a reel; microfiche on a flat sheet. Needs a special reader (pictured) to read them.
Cuts down storage space for eg newspapers in a library,. |
| Sound output |
 |
...using speakers. Useful for music;
voices and sound effects for games; spoken warnings in cars; telephone banking.
Also used on MIDI keyboards. |
| Control signals |
 |
Computers in control
systems will send out control signals to activate devices. |