|
Computer Languages |
|
Low level (Assembly) languages...
- are closely related to the design of the computer
- are
difficult for programmers to develop code and to test and modify
programs. Simple tasks need a lot of instructions.
High level
languages
...
- use instructions related to the way a problem is solved
- are easier for programmers to design, code, debug and maintain.
- started to be developed in the mid 1950s.
Some examples of high-level languages:
- FORTRAN (FORmula TRANslator); mainly used for
engineering/scientific computing.
- COBOL(Common Business Orientated Language). Still
one of the main commercial data processing languages.
- ALGOL (ALGOrithmic Language) was also developed
in the 1950s and many of the languages such as
C and
C++ are developed from it.
- BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction
Code) was developed in the 1960s as a simple programming
language.
- PASCAL was developed in the 1970s as a
well-structured teaching language.
- Other high-level languages include :
LISP,
PROLOG,
PL/1 ,
ADA
|
|
| |
|
Procedural (Imperative)
Languages.
In procedural languages a sequence of commands is given. Each command is an
action which needs to be carried out. Traditional languages such
as FORTRAN, COBOL,
BASIC and PASCAL are
procedural languages.
Procedural languages use variables and
program flow control (loops, subroutines etc).
|
|
| |
|
Non-procedural (Declarative)
Languages.
A set of facts
and a set of rules is declared - from which, information is
deduced. Declarative languages consist of logic languages
(eg PROLOG) and functional languages
(eg LISP).
PROLOG is particularly suited to developing expert
systems.
- a program consists of a number of facts
parent(Tom, Bob)
parent(Pam, Bob)
male(Tom)
and a set of rules
father(X,Y) :=
parent(X,Y)
male(X)
brother(X,Y) :=
parent(Z,X)
parent(Z,Y)
male(X)
and a query which is answered by applying
the facts and rules eg
? father(who, Bob)
which would return the answer
who = Tom
LISP is useful for programming AI (Artificial
Intelligence) systems.
LISP stands for
LISt Processing. It is an example of a functional
language, and a LISP program consists of a series of function
definitions.
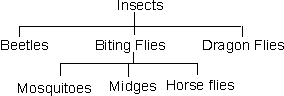
Example : The
statement
(insects(beetles
biting_flies (mosquitoes midges horseflies) dragon_flies))
is a representation of the hierarchical
diagram :
|
|
| |
| |
Object-oriented
Languages.
Objects have properties
and methods.
C++ is an example of an object-oriented programming (OOP)
language. Most application developing languages (eg
Visual Basic, Delphi) use objects.
In Visual Basic, the programmer places
objects on forms and defines the properties of each object. It is
an event-driven language. An event is eg a click of the mouse and
this initiates a sequence of code to be executed. The behaviour
of an object when an event occurs is programmed, and every object
has a number of methods - procedures which it can execute.
A Class defines the methods and
properties for a group of similar objects.
A 'Jumbo jet' is an instance of an object
'Aeroplane'. Its properties are its length, width, height, colour
etc and its methods are flying, landing, turning etc
|
|
| |
| |
Visual Languages
Some object-oriented languages allow the programmer to
develop an application by creating new objects or by placing
previously-defined
objects into a windows-based (GUI) environment and setting the ways the objects
interact.
Eg Visual Basic, Visual C++, Delphi...
|
|
| |
|
Other Languages.
Some high level languages are written for
special purposes.
ADA is used for programming embedded systems - hence
the interest by the Department of Defence for using it to program
missile systems.
OCCAM is a language specially developed to program
parallel processing systems eg on transputers.
Example:
par {enables two processes to
execute simultaneously}
seq
a := 20
b := a * a
seq
c := 1
d := 2 * c
parend
PL/1 (Programming Language 1) was developed to combine
the best features of a scientific language and a commercial
language but ended up by being too complex.
|
|
| |
| |
Scripting languages allow a user some
flexibility in some applications. Examples
: Javascript and VBScript
allow a user to program some functionality into a web page. This is demonstrated
in the Activities on some of these tasks.
|
|
| |
| |
Package-based Languages.
Some packages eg Microsoft Access
have in-built programming capabilities. This allows the programmer to customise
general purpose packages to exactly meet the needs of the business.
These are also called Fourth Generation Languages
(4GL). Facilities include searching, data manipulation and report
generation.
|
|
| |
| |
Markup Languages A language that
describes how a document is laid out. Normally use
tags.
Examples :
HTML - used for defining how a
web page should be displayed by a browser.
XML - defines the structure of
data that can be used by different software.
|
|
 |
| |