Text based
(command line) |
The
user types in commands. |
|
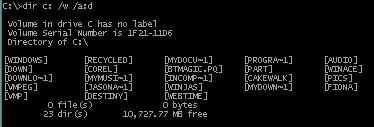
Eg
: MS-DOS interface.
DIR C: /W /A:D
will list all the directories in the root directory of drive C in wide
list format.
Disadvantage
is that commands need to be known, typed and spelled correctly.
Advantages
- versatile as a number of different 'switches' can be used to moderate
the command. |
| |
Dialogue boxes
(Forms) |
An on-screen form is displayed
and the user has to enter data and select options using text boxes, radio
buttons, drop-down boxes etc.. |
|
The user does not have to
learn commands. Easy-to-use method which avoids ambiguous or invalid data
being entered - most drop-down boxes only allow the options listed to be
selected. |
| |
| Free format dialogue |
Text can be entered
in a special form. |
| This
is used by some 'Help' programs and some search engines on the Internet. |
| |
GUI
(Graphical User Interface) |
Uses windows,
icons representing options which can be selected using a (mouse)
pointer. Also has menus available. |
| Intuitive
and 'user-friendly' method. Suitable for users with lower IT skills. A
number of different applications will use the same icons and methods - so
each one 'feels' the same. |
| |
| Dedicated keys |
Some keys or
combinations of keys may perform pre-defined tasks. |
| Eg
<CTRL> and <S> may save a piece of work.
<CTRL> <ALT>
and <DEL> may re-boot a computer.
|
| |
| Soft keys |
It may be possible
to program keys to perform tasks when pressed.. |
| Some
keyboards may have programmable 'function' keys. |
| |
| Pointing devices |
Manipulating a
device which moves a pointer on the screen. |
| Examples
: Mouse, Tracker ball, Joystick, Graphics Pad and Light Pen/Puck. |
| |
| Speech recognition |
Microphone
used to receive speech input. Speakers used for speech output. |
Problems:
- Users may speak
different languages;
- Regional accents may not be
recognised;
- Some words sound the
same - two, to, too;
- Users may have health problems (eg a cold)
that alter the quality of the voice
Developments are being made
to produce a natural
language interface
- where the user can talk naturally to the computer to give instructions
eg using natural language of humans, slang expressions etc. This is really
in the field of AI (Artificial Intelligence) and is a difficult problem
due to the complexity of language. |
| |
| Handwriting |
Some hand-held
computers allow users to 'write' on the screen. |
| Complex
software needed to recognise different people's handwriting. |
| |